Why Trusted Data is the Linchpin of ERP Modernization
As businesses grow and evolve, it can be challenging to manage the complex data landscape with a traditional ERP system in place. The data generated by day-to-day business operations has exponentially increased over recent years. In fact, a recent Informatica survey shows that 55% of CDOs report having over 1,000 sources of data in their organization1.
In this sea of transactional, analytical and streaming data, enterprises are leveraging different legacy ERP platforms, such as SAP ECC, to store it. However, legacy systems generally are not fit to drive digital transformation initiatives. They often have scalability issues, rigid workflows, limited reporting and analytics capabilities, little maintenance support, poor user experience and integration challenges with cloud applications.
According to Gartner™ “By 2024, more than 60% of organizations will deploy cloud ERP as an ecosystem of application and technology platforms from multiple vendors.”2
Increasingly, enterprises are looking to capture the new market potential provided by the latest ERP solutions by modernizing their systems. From improved business process efficiency to reduced operational costs and innovations that drive business growth, ERP modernization can provide the business agility that enterprises need. And that is why data executives are starting to recognize it as a high priority.
ERP Modernization Challenges
ERP systems are used to manage business functions such as finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, sales and more. However, the effectiveness of an ERP system depends on the accuracy and reliability of the data housed in it. ERP modernization may sound as simple as migrating data from a legacy ERP system to a more advanced one. However, enterprises need parameters to measure success.
Three key metrics to track are:
- Time: Enterprises need to complete any modernization project within the expected timeline with minimal disruption to their day-to-day business. But ERP modernization programs can go awry and exceed the estimated timeline without the right set of data strategies.
According to the 2023 ERP Report by Panorama Consulting, more than 42% of ERP projects ran overtime and around 31% of executives called out data issues as a top reason for delays.3
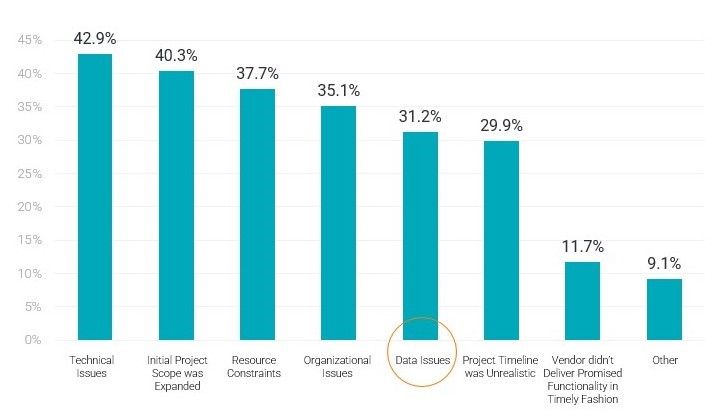
Figure 1: Projects get delayed for several reasons, including data issues, according to the 2023 ERP Report by Panorama Consulting.
At a minimum, your business users need access to high-quality and up-to-date data to make the most out of your ERP investments. But if data quality issues are not handled before an ERP migration, they could compound and take a significant amount of time and effort to fix in your new ERP system.
Similarly, different legacy ERP applications typically have separate reference data and hierarchies. You need a mechanism to standardize these while migrating to newer systems to stick to the project timeline.
Enterprises usually leverage disparate ERP systems for different lines of business. The separate systems can help keep an individual department accountable for their own data and use that data to inform initiatives. However, these systems must talk to each other to provide a consolidated view of reporting for management and inform key decision-making.
For example, the human resources team must be cognizant of the finance function to ensure they have proper funding before initiating a new hiring strategy. This is where data integration capabilities come into the picture. You need to integrate data across various legacy ERP systems, such as SAP ECC or Oracle EBS, to provide your data consumers with a consolidated and accurate view.
- Cost: This key parameter matters greatly to chief data officers (CDOs) / chief technology officers (CTOs) when evaluating technology investments. While enterprises usually focus on evaluating whether a new ERP vendor is the right budget fit technology-wise, they must also consider the amount of data being migrated. For example, if a legacy system contains duplicates, it will cost more to migrate and maintain those duplicate records in the new ERP system.
According to Panorama Consulting’s 2023 ERP Report, around 47% of the ERP projects were over budget, wherein more than 33% of the executives cited data issues as the primary contributor to budget overruns.
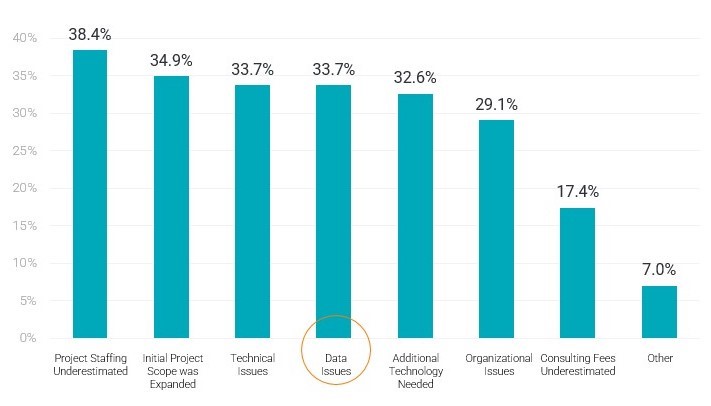
Figure 2: Data issues were one of the top reasons cited for budget overruns, according to the 2023 ERP Report by Panorama Consulting.
This is why enterprises need to make sure they are working across ERP landscapes to create a 360-degree view of their master data. By carefully studying the target ERP landscape, enterprises can avoid costly data integration technology investments by providing an API-based connection in the target ERP. This gives the target ERP access to data from other heterogeneous ERP systems.
- Risk: You need access to governed data in ERP systems to eliminate any risks related to compliance, data security or privacy. Data dependencies also pose a challenge if all the required data is not migrated to the desired ERP platform at once. Not evaluating the source and target systems for the type of data that can be successfully migrated can also be a threat to timely modernization.
Because ERP systems need to be accessed by a wide range of stakeholders, it’s critical to provide role-based access control. A robust data governance policy must be in place to make sure all eligible business users have seamless access to the data they need. At the same time, these policies will also help ensure data security and privacy by defining what data can be shared outside the organization, user groups, required level of approvals and more.
Without a consolidated view of enterprise data enabled by master data management (MDM), a robust data governance policy and access to data integration capabilities across ERP systems, organizations run a risk of making poor decisions based on inconsistent and poor-quality, siloed data.
How Do Data Management Capabilities Help?
For any modernization program, enterprises should look for solutions that provide an array of data management capabilities, including data integration, data governance, data quality and MDM. Enterprises will benefit from the scalability, interoperability and ease of use while getting access to all these capabilities in one platform.
Data discovery: To start, enterprises must perform data discovery by performing thorough due diligence and assessments of their source and target systems. Scanning and profiling upfront can help you reduce the overall modernization time and cost. It can also enable you to improve decision-making.
For example, scanning source applications can help you understand which datasets can be migrated easily without disruption because they have a lower dependency on business operations. Profiling of datasets can uncover any compliance risks associated with data sharing or related datasets that must be co-migrated for data consistency.
Data quality: Data quality assessment and remediation play a critical role in any modernization effort. It’s essential to maintain data quality before migrating data to target systems and to bring over only high-quality data. Built-in, automatically generated data quality scorecards can help you determine the data quality level of the source data for a migration. If existing low-quality data is brought into a target system, you may not be able to use that data for effective decision-making.
Data stewardship and data governance: Beyond quality data, data stewardship and data governance help ensure that your data is of value to users throughout the data lifecycle — from creation to disposal — and compliant with industry standards. Data stewardship goes a step further than data quality to impact the overall effectiveness and health of data spread across the organization. Data governance provides seamless access for your data consumers to good-quality data.
By regularly assessing the data assets in ERP systems and carefully measuring them against established data quality standards, data retention policies and data governance frameworks, data stewards can ensure compliance of enterprise data across ERP systems. This helps guarantee that the data is governed, fit for purpose, remains relevant and doesn’t pose any future compliance risks if new regulations or policies are introduced.
Master data management: MDM helps ensure that the data across your ERP systems is accurate, complete and consistent across all departments and functions, regardless of where it lives. It centralizes key master data domains — such as customer, supplier, product and more. It also reduces the complexity of managing multiple data onboarding points.
By rationalizing data across ERP systems, MDM enables the creation of a single, trusted view of data. It also uncovers the hidden relationships among various master data domains. MDM empowers business users with access to high-quality, relevant data, enabling them to make more-informed business decisions.
For example, with MDM, businesses can gain a better understanding of their customers by consolidating customer data from multiple sources. This could include sales, marketing, customer service and support to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences and needs. This in turn allows businesses to create products and services that better suit customers’ needs, improving satisfaction and loyalty.
MDM also helps businesses to optimize supply chain operations by consolidating data about suppliers, inventory and logistics. This gives businesses a complete picture of their supply chain and helps identify any inefficiencies or opportunities for improvement. For example, narrowing down the available suppliers and delivery routes a company uses can help them select a preferred supplier.
Compliance and risk management is another pillar where MDM plays a critical role. By ensuring that all data is accurate, complete and up-to-date, businesses can meet regulatory requirements and reduce their exposure to risk. This can be especially critical in industries such as healthcare and finance, where data security and compliance are paramount.
Best Practices to Adopt in ERP Modernization Programs
- Leverage augmented data management techniques: For large-scale ERP modernization programs, keeping track of all the data and program management initiatives can be overwhelming. Hence, enterprises must leverage augmented data management techniques, which use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to automate various data management processes. These include such as data profiling, data quality assessment, match and merge, data integration and others. In addition, augmented data management can help provide advanced analytics and insights into data quality and data usage, enabling you to make more informed decisions.
For example, early information about common data quality issues can help you properly plan a migration effort and focus on fixing those data issues. Some data value correlations can also provide insights that are critical to business growth.
- Provide data context: Data management tools and service providers make the path to ERP modernization easier. But human intelligence also plays an integral role, as business stakeholders are the ones that need to understand the data. So, it becomes intrinsically important to provide the ability to understand the data context within the ERP tool, too.
- Enrich ERP data as appropriate: Enrichment of master data across domains ensures that new data is accurate, comprehensive, and up to date across the ERP landscape. For example, retail companies can better plan their advertising strategy if their sales and product data is enriched with market data around upcoming holiday seasons.
Customer Success Story: Building Materials Company Gains ERP Efficiency
One of the largest retailers and distributors of building materials in Europe operates with various sub-companies and business units, which use different ERPs and product management solutions. Wanting to become a data-driven organization, the company decided to leverage SAP S/4HANA as a backbone to modernize their landscape. They also wanted to build a future architecture that could accommodate product data across all of their business units.
Informatica identified the need to establish an MDM solution that utilizes a standard data model to gather product information across business units. A central MDM was created with match and merge rules, which now centrally govern 100 to 200 product attributes.
The centralized MDM solution has provided efficiency for future growth by mergers and acquisitions, expanding their business, decreasing operational costs, increasing procurement efficiency and improving cross-sell, upsell and online sales with better customer and product insights.
Next Steps
MDM, data quality, data governance and data integration capabilities have proven to be critical to accurate decision-making, driving operational efficiency and innovation. So, enterprises must ensure that these data management capabilities are intrinsically rooted in their broader ERP modernization efforts.
The Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud (IDMC) is a one-stop shop for a range of data management capabilities. Powered by our AI engine, CLAIRE, IDMC provides the data intelligence and context that organizations need to innovate and succeed in their ERP modernization programs.
Learn more about modernizing your ERP by reading our solution brief, “Accelerate ERP Modernization with Trusted Data.”





